5 Common pitfalls in scientific writing and how to avoid them

Does the task of writing make you nervous? Especially for non-native English authors, scientific writing can be a challenge. Whether you are writing a research proposal, a manuscript, or a cover letter, errors in writing can render your communication ineffective. Being aware of some of the most common pitfalls in scientific writing can help you avoiding them.
1. Redundancy
Redundancy refers to repetition of words and phrases. Repetitious writing leads to wordiness and impaired comprehension. Moreover, it can make reading tiresome and can be distracting to readers. One of the most common ways in which authors repeat themselves is by paraphrasing and presenting in text the information already given in a table. Another common form of repetition is presenting in the abstract the information that is mentioned in the title.
2. Vocabulary
Have you ever experienced the struggle to understand an author’s thoughts while reading any literature? Having a good vocabulary can have a huge impact in making your writing impactful. Choosing the right words to express an idea or a thought helps readers’ comprehension and also establishes your proficiency over language.
3. Abbreviations
Abbreviations are shortened forms of words and phrases. They are commonly used in manuscripts to make complex technical writing more concise and easier to read. However, they can also make communication unclear if used without care. There are some best practices associated with the usage of abbreviations.
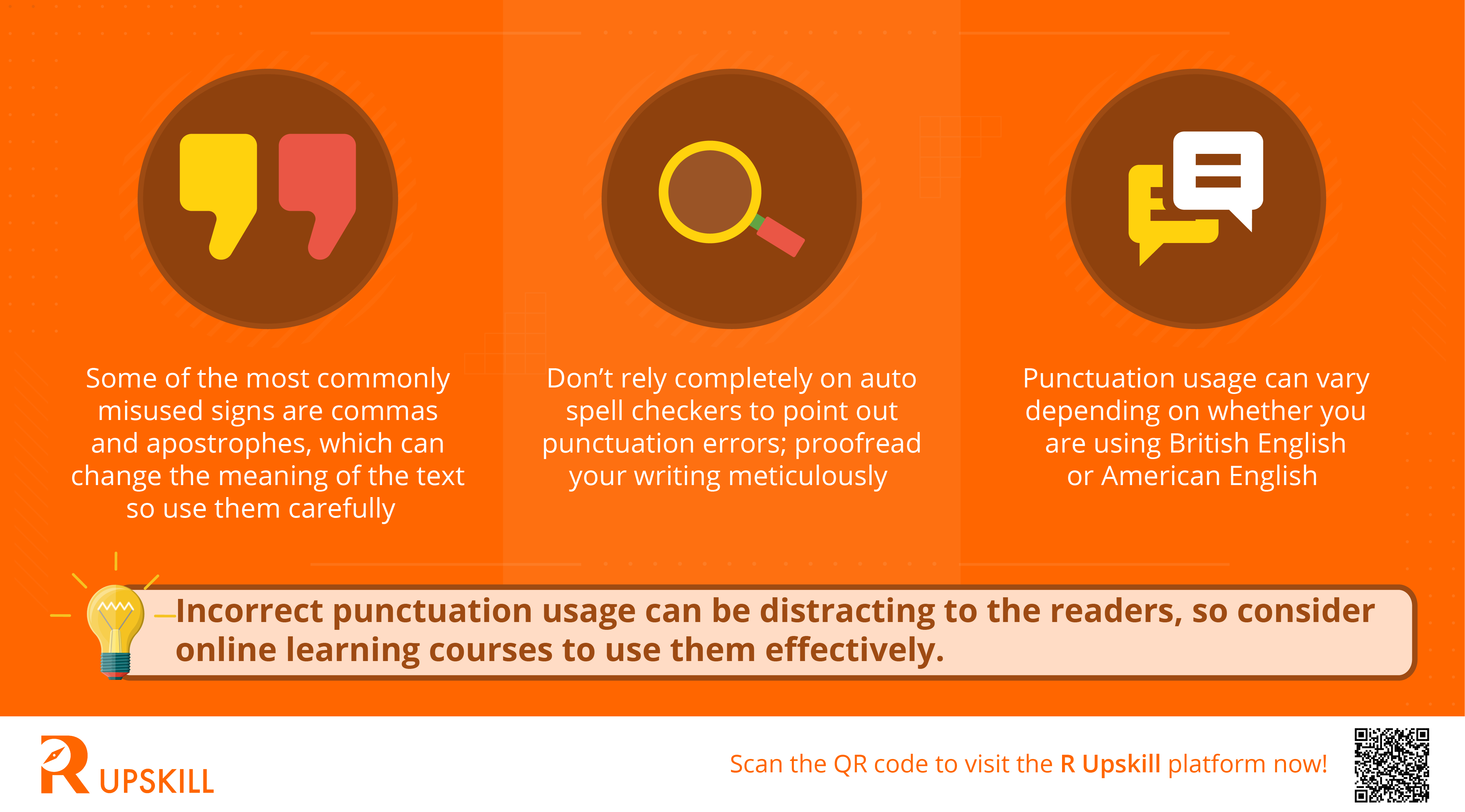
4. Punctuation
Think of punctuation as the traffic signals of the written word. They make the job of reading easier by indicating a break in thought, pauses, emphasis, or more. Using punctuation accurately is crucial in building a strong case for your study. Moreover, incorrectly used punctuation can divert readers’ attention. Here are some quick tips on using punctuation effectively.
5. Tone
Tone refers to the author’s voice which reflects in their writing. Academic writing is formal, so the tone of writing should indicate it. While it is best to avoid any informal language usage, you should also ensure that your writing style is not tedious and jargon-heavy. Here are some tips on maintaining a balanced tone.
Can you improve your writing skills and your manuscript’s chances of acceptance? YES!
Writing skills are important for a researcher to succeed. It is never too late to learn to write better and empower yourself. You can now access the best resources and learn from experts with R Upskill, which is the largest collection of learning programs for researchers.
With courses that help researchers at any stage of their career to write better research proposals and manuscripts, correspond with journal editors with ease, and become more confident in research writing in general, you can take your writing skills to the next level with R Upskill. You can access academic writing courses along with all of the 80 programs for researchers with a single subscription to the All Access Pass. Check it out now!
How does R Upskill help you?
With 80+ programs created by academic leaders, you’ll find courses and guides for every challenge you may face, be it academic publishing, funding, research promotion, or dealing with mental stress.
A single subscription to R Upskill All Access Pass will enable you to take up any courses you wish and access to a personal mentor who will guide through every challenge.
Here’s how R Upskill All Access Pass can boost your chances of success